Sweet Potato Nutrition Facts: So you think sweet potatoes are just a tasty side dish? Think again! These vibrant tubers are nutritional powerhouses, packing a serious punch of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. From boosting your immune system to improving digestion, sweet potatoes offer a surprisingly wide range of health benefits. Let’s dive into the delicious details and uncover why this humble spud deserves a starring role in your diet.
This guide breaks down the nutritional composition of sweet potatoes, exploring everything from their macronutrient profile to their impressive vitamin and mineral content. We’ll also delve into the glycemic index, exploring how sweet potatoes affect blood sugar levels and discussing the impact of different cooking methods. We’ll even cover the various sweet potato varieties and their unique nutritional benefits, offering tips for preparation to maximize nutrient retention.
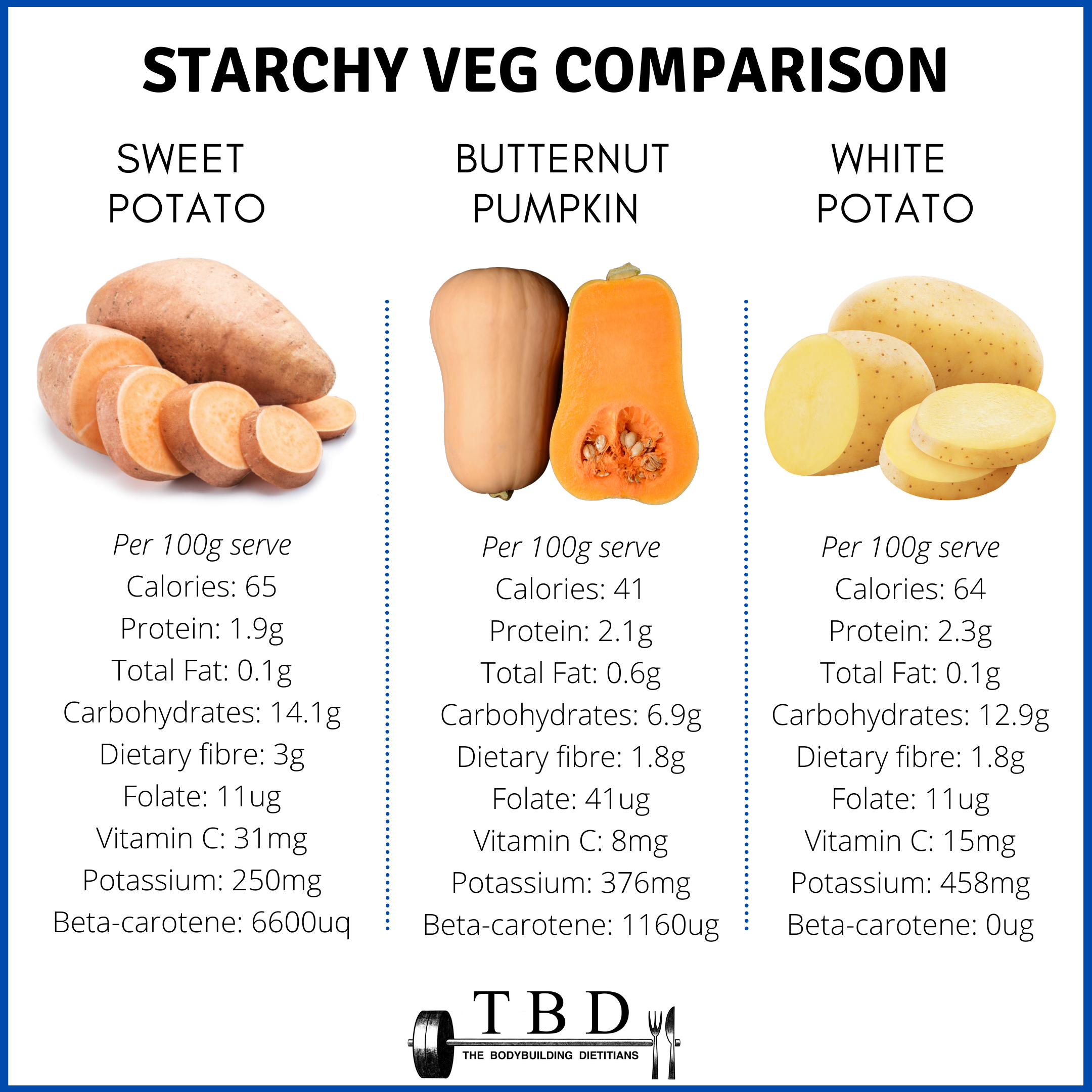
Sweet Potato Nutritional Powerhouse
Sweet potatoes, often overlooked as a simple side dish, are nutritional dynamos packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This versatile root vegetable offers a delicious and healthy addition to any diet, providing a range of benefits for overall well-being. Let’s delve into the nutritional composition, health benefits, and preparation methods of this underestimated superfood.
Nutritional Composition of Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes boast a remarkable nutrient profile, offering a good balance of macronutrients and a wealth of micronutrients. A typical serving size (approximately one medium sweet potato, about 130 grams) provides a significant contribution to your daily nutritional needs.
| Serving Size (approx. 130g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| One medium sweet potato | 27-30 | 2-3 | 0.2-0.3 |
Beyond the macronutrients, sweet potatoes are rich in essential vitamins and minerals:
- Vitamin A (Beta-carotene): An excellent source, crucial for eye health and immune function.
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant, supporting the immune system and collagen production.
- Potassium: Important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and fluid balance.
- Manganese: A vital mineral involved in bone health, metabolism, and wound healing.
The high fiber content in sweet potatoes (approximately 3-4 grams per serving) promotes healthy digestion, aids in regularity, and contributes to feelings of fullness, which can be beneficial for weight management.
Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Impact
The glycemic index (GI) of sweet potatoes is moderate, typically ranging from 44 to 54, depending on the variety and cooking method. This means they cause a slower and more gradual rise in blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods like white bread or sugary drinks. However, it’s higher than some other starchy vegetables like green beans or broccoli.
Cooking methods influence the GI. Boiling tends to increase the GI slightly compared to baking or roasting, which retain more of the fiber, slowing down the absorption of sugars. For individuals with diabetes, choosing lower-GI preparation methods and controlling portion sizes are key to managing blood sugar effectively. While sweet potatoes can be part of a diabetic diet, careful monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential.
Health Benefits of Sweet Potato Consumption
The impressive nutritional profile of sweet potatoes translates into numerous health benefits. Their rich vitamin and mineral content supports various bodily functions and contributes to overall well-being.
Browse the multiple elements of mendocino craiglist to gain a more broad understanding.
An infographic illustrating sweet potato benefits for different age groups and health conditions could feature:
- Visual: A stylized sweet potato with branching lines representing benefits. Each branch could be color-coded by age group (infant, child, adult, senior) or health condition (immune support, eye health, digestive health).
- Data: Concise descriptions of benefits for each group/condition (e.g., Vitamin A for eye health in infants, fiber for digestion in adults, antioxidant protection against chronic diseases in seniors).
Sweet potatoes’ antioxidant properties, particularly beta-carotene, contribute to their potential role in preventing chronic diseases like heart disease and certain cancers by neutralizing harmful free radicals.
Sweet Potato Varieties and Nutritional Differences
| Variety | Key Nutrient Differences | Typical Taste Profile | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orange | High in beta-carotene (Vitamin A) | Sweet, slightly earthy | Mashed, baked, roasted |
| Purple | Rich in anthocyanins (antioxidants) | Sweet with slightly nutty notes | Roasted, grilled, in salads |
| White | Milder flavor, lower in beta-carotene | Subtle sweetness, slightly creamy | Mashed, boiled, in soups |
Taste and texture vary significantly. Orange sweet potatoes are generally the sweetest and most intensely flavored, while white sweet potatoes have a milder, more subtly sweet taste. Purple sweet potatoes often have a slightly earthy or nutty undertone.
Sweet Potato Preparation and Nutrient Retention, Sweet Potato Nutrition Facts
Different cooking methods affect nutrient retention. To maximize nutritional value, consider these points:
- Boiling: Some water-soluble vitamins may leach into the water, but it’s a quick and easy method.
- Baking: Retains more nutrients than boiling, and enhances sweetness.
- Roasting: Similar to baking in nutrient retention; brings out natural sugars and creates a caramelized flavor.
- Microwaving: Fast, but can result in slightly less nutrient retention than baking or roasting.
Preparing sweet potatoes as mashed, fried, or baked influences nutritional value. Frying adds unhealthy fats, while baking or mashing (without added fats) preserves more nutrients. To maximize nutrient retention, aim for minimal processing, avoiding peeling whenever possible (unless necessary for texture), and using cooking methods that minimize water loss.
Closing Notes: Sweet Potato Nutrition Facts
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
Sweet potatoes aren’t just a delicious treat; they’re a smart choice for anyone looking to boost their health and well-being. From their impressive vitamin A content to their fiber-rich goodness, sweet potatoes offer a diverse range of benefits that support everything from eye health to gut health. So next time you’re at the grocery store, grab a bag of these nutritional gems and start reaping the rewards! Experiment with different varieties and cooking methods to find your favorite way to enjoy this versatile and healthy vegetable.